PostgreSQL
This section explains how to create, configure, and test a PostgreSQL data source in DataDios.
Steps to Create and Test a PostgreSQL Data Source
Step 1: Create a Data Source
-
Navigate to the Data Sources tab in DataDios
-
Click + CREATE DS
-
From the list of available data source types, select PostgreSQL
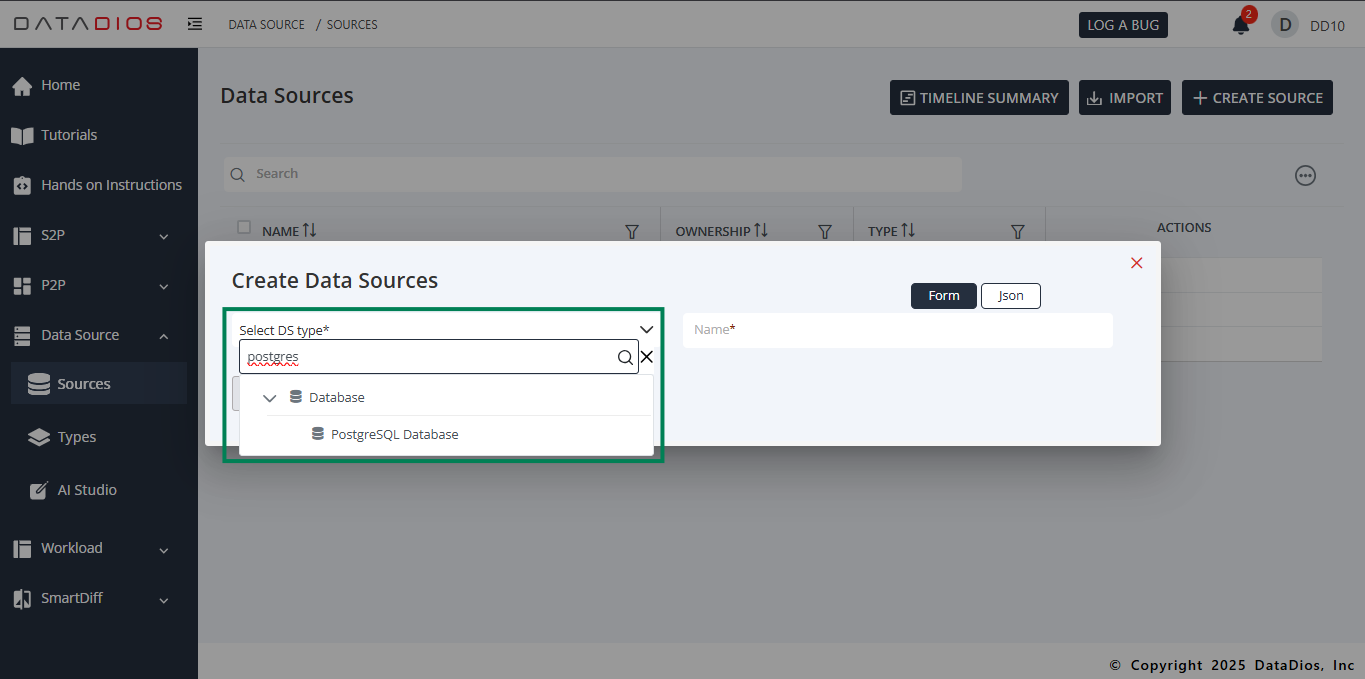
Step 2: Fill Connection Details
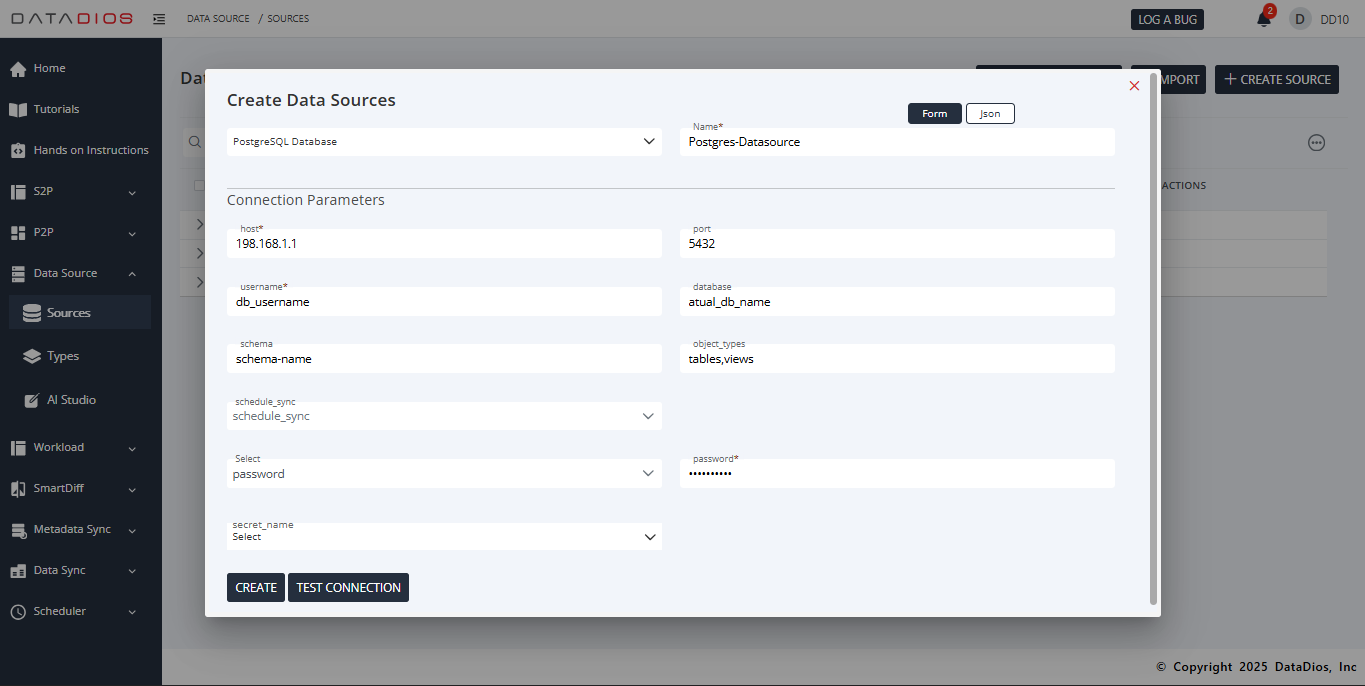
In the Connection Details form, provide the required parameters:
-
Group: (Optional) Grouping for data sources
-
Host: PostgreSQL host or IP address
-
Port: PostgreSQL port (default:
5432) -
Username: PostgreSQL login username
-
Password: PostgreSQL login password
-
Database Name: Database to connect to
-
Schema: Target schema (leave blank to use the default schema)
-
Object Types: Choose whether to fetch
tables,views, or both -
Schedule Sync: Configure for metadata timeline synchronization (see Metadata Sync)
-
Secret Name: (Optional) Reference to secret stores (e.g., AWS Secrets Manager, Azure Key Vault)
- JSON Structure
{
"group": "",
"host": "198.168.1.1",
"port": "1433",
"service_type": "",
"username": "sql-admin",
"database": "QuickStart",
"schema": "diff_test",
"object_types": "",
"password": "Admin@123"
}
Step 3: Test Connection
-
After entering details, click Test Connection
-
Ensure the connection is validated successfully
Step 4: Save Data Source
- If the test succeeds, click Create to save the data source
- You will be redirected to the Datasource Listing Page, where the PostgreSQL data source will appear
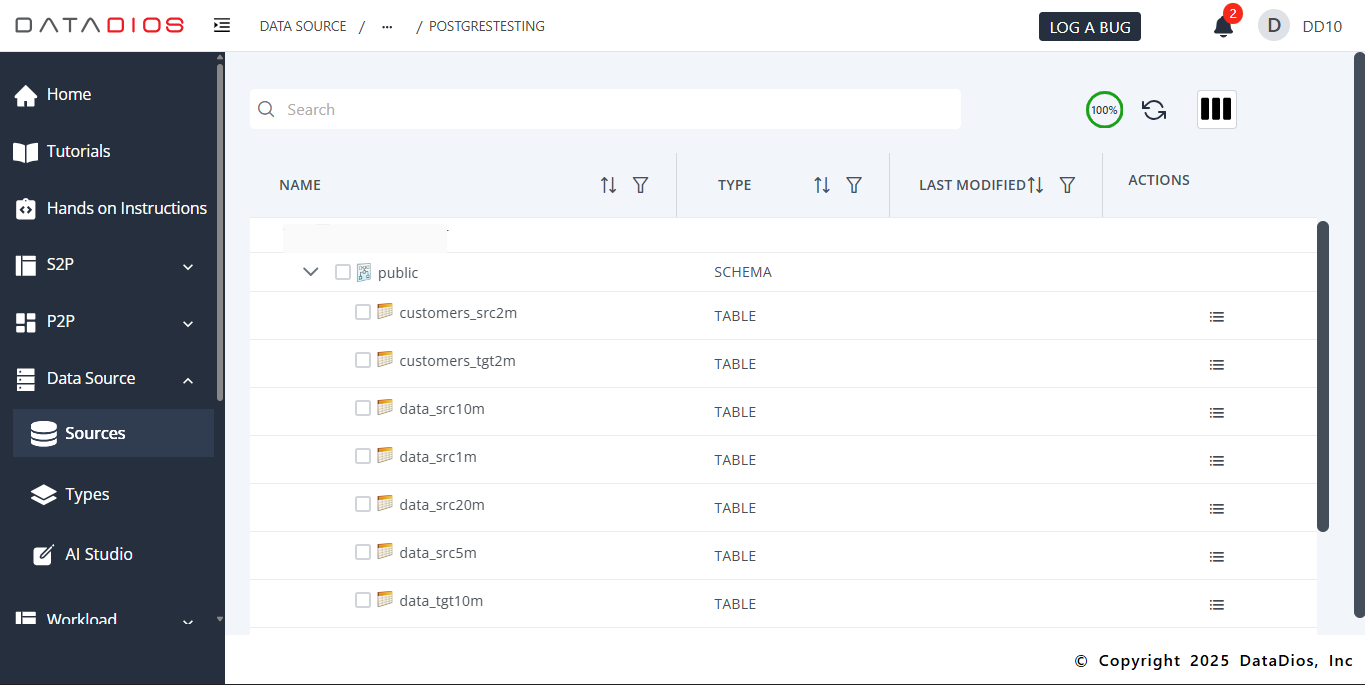
Step 5: Explore Data Source Items
-
Expand the PostgreSQL data source to view all items (tables, views, etc.)
-
To view metadata about any item:
- Click the item name
- Click the three stacked lines icon to open the Object Metadata pop-up
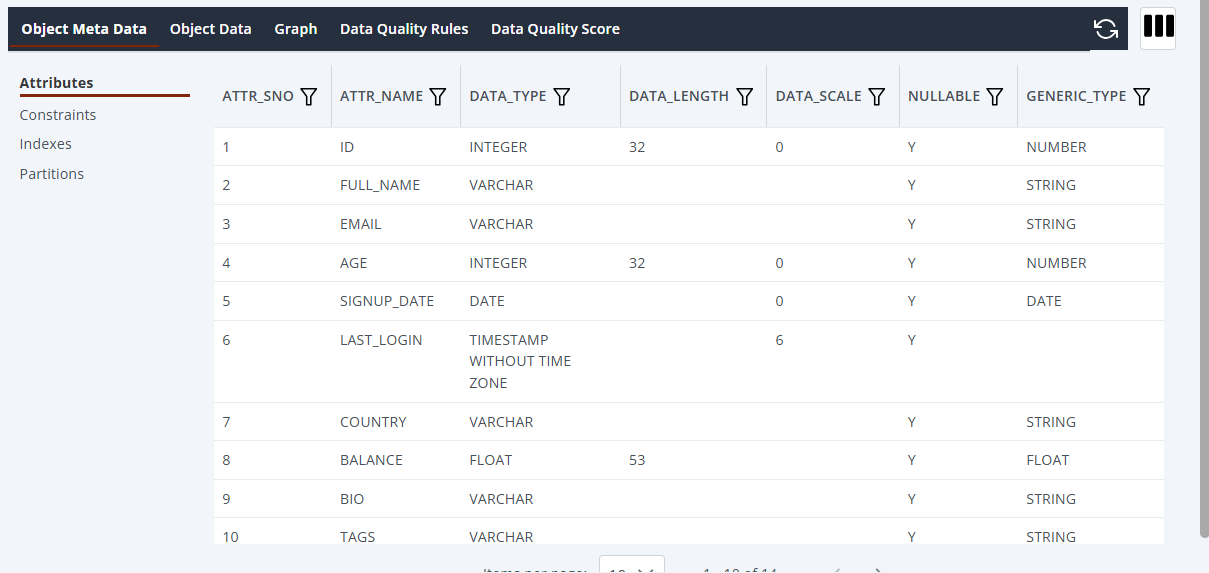
-
You can also explore additional features in the Metadata Explorer:
-
Object Data
- View the actual data present in the selected resource (e.g., table rows or file details)
-
Graphs
- Visualize dependencies and relationships across schemas
- See how the item is connected to databases or other schema objects
-
Data Quality Rules
- Review applied data quality rules and scores
- For detailed information, refer to the Data Quality documentation
-
Best Practices
- Use Secret Store for passwords to avoid hardcoding credentials
- Always Test Connection before saving to ensure configuration is correct
- Organize with Groups for easier management of multiple PostgreSQL data sources
- Leverage Schedule Sync to keep metadata timelines updated
For more details on configuring PostgreSQL with metadata sync, see the Metadata Timeline.